Cold vs. Flu: Know the Difference
With cold and flu season upon us, it’s important to understand the difference between cold vs. flu...
By: Reliant Urgent Care May 6, 2021 2:00:37 AM
A concussion is a serious injury that shouldn’t be taken lightly. If you want to know what concussion signs to look for, read on to learn about observable symptoms, how to treat a concussion and when to seek help from a healthcare provider.
Concussions are caused by a bump or blow to the head. Getting hit in the head in a full-contact sport, car, motorcycle, and biking accidents, or falls where you hit your head can all cause concussions. When forceful enough, a concussion can cause your brain to move inside your skull, leading to a traumatic brain injury and an array of symptoms. Those who have had one concussion are also more at risk for severe concussions following a second blow to the head.
There are several signs of concussion and associated symptoms to watch out for following any blow to the head, with some more obvious than others. Sometimes bruising, bleeding, or a visible wound is also observed, but not always. Concussion symptoms can be more subtle.
Concussion symptoms often reported by patients include:
Common signs and symptoms of concussions that can often be observed physically include:
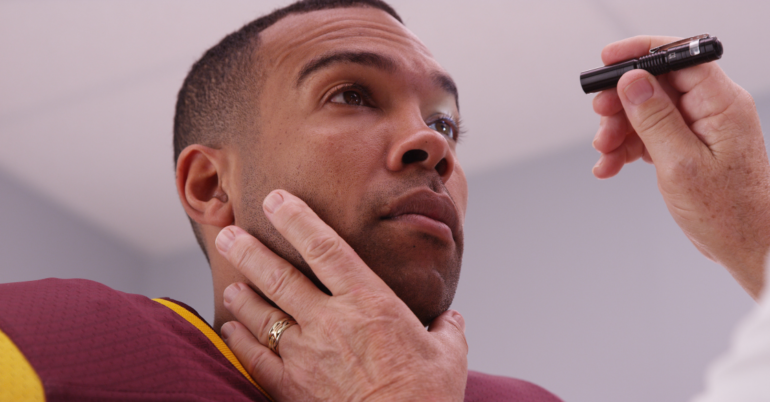

Signs of concussion considered danger signs include:
Anyone experiencing the danger signs described above should seek medical attention immediately.
Symptoms that aren’t present immediately after brain trauma don’t mean that you won’t have symptoms down the line. Some concussion patients will require long-term treatment plans for symptoms like sleep problems, issues with concentration, or other impacts to brain function if they have suffered a severe concussion or are experiencing their second concussion. It’s essential to be in communication with your healthcare provider following any head injury.
Those experiencing mild concussion symptoms may be given instructions to follow by a healthcare professional during a virtual appointment rather than seeking emergency care at a medical facility. It’s important to monitor signs of concussion and any present symptoms closely, as the situation can change quickly, requiring additional care. Experts agree that having someone there with you following a possible concussion event is an important course of action, as you may not be able to monitor your symptoms as closely on your own.
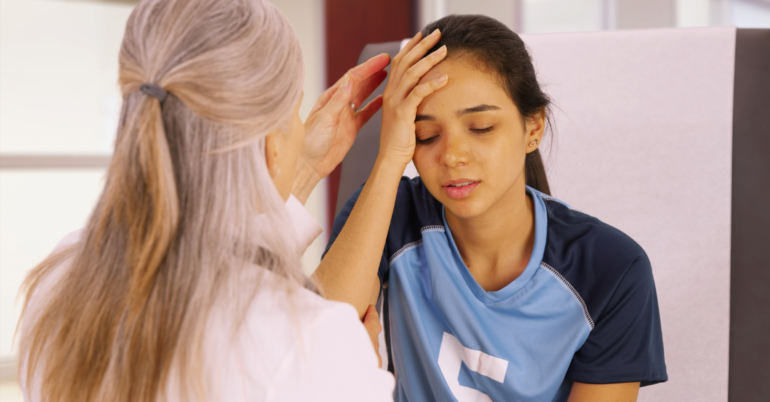

Once you’ve followed up with a healthcare provider, common treatments for mild concussions include:
With athletes, concussion protocols typically require clearance from a medical professional before returning to the sport. Follow the same logic and avoid any situations where you’re putting yourself at risk for a second brain injury, as a second concussion can lead to longer-term problems, even brain damage.
If you find that your symptoms aren’t going away, it may be time to seek additional concussion treatment in Los Angeles and help from a medical professional.
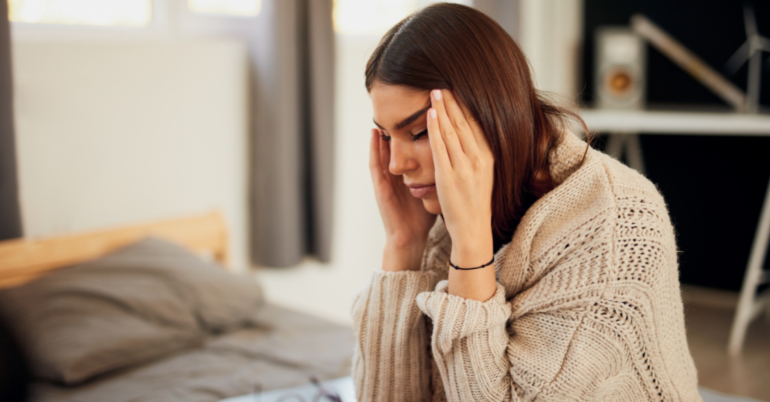

There are three types of concussions: mild, moderate, and severe. Severe concussions include a loss of consciousness, even if just for a few seconds, alongside any of the danger signs described above. That level of trauma warrants immediate urgent care.
Those with symptoms that go away after a short time may choose to monitor symptoms while they book a follow-up appointment with a physician. Book your urgent care appointment online or visit us at one of our Los Angeles urgent care locations if you are experiencing signs and symptoms of a concussion. The health professionals at Reliant are available to talk through any symptoms virtually or arrange an in-person visit to address your concerns.
With cold and flu season upon us, it’s important to understand the difference between cold vs. flu...
A new variant has changed how the country is approaching COVID-19, but that doesn’t mean the...
You’re feeling awful. You have fever not responding to over the...